Acoustic Bipole and Tripole

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
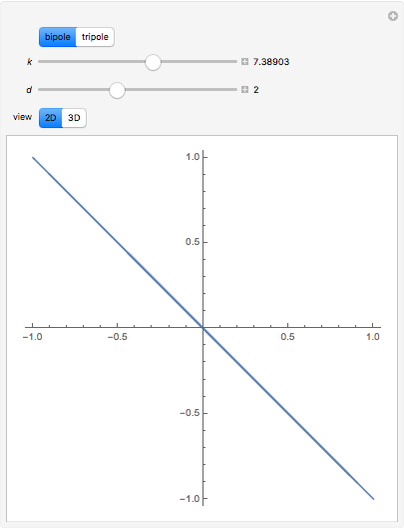
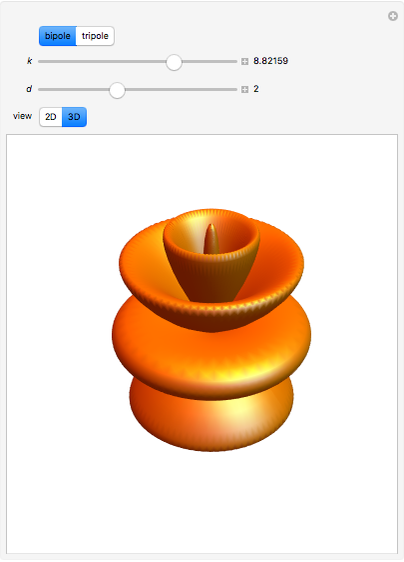
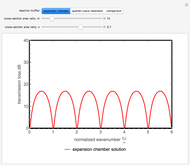
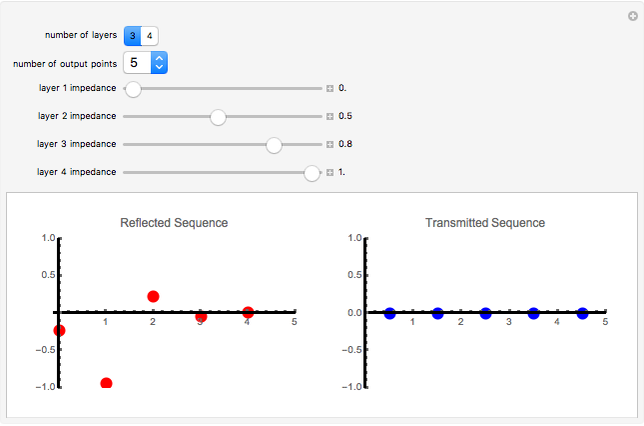
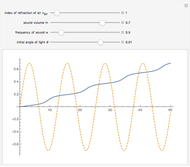
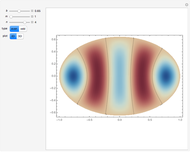
An acoustic bipole consists of two identical monopoles driven in phase (whereas, in a dipole, they are out of phase), separated by a short distance  along the
along the  axis. As shown in the Details section, the radiated sound produces a directivity pattern
axis. As shown in the Details section, the radiated sound produces a directivity pattern 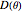 , where
, where  is measured between the point of observation and the normal of the bipole and
is measured between the point of observation and the normal of the bipole and  stands for the wavenumber.
stands for the wavenumber.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (January 2014)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
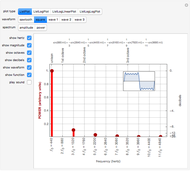
The radiation field for a bipole is
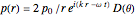 ,
,
where the directivity pattern can be written as
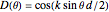 .
.
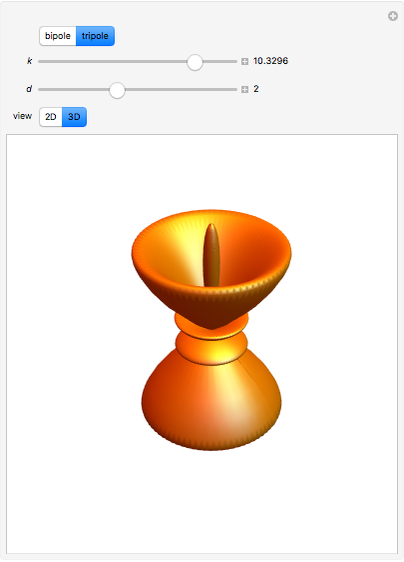
For the tripole
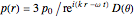
and
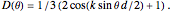
See Part 6 of [1].
Reference
[1] P. B. Nagy. "Acoustic Radiators." (Nov 9, 2001) www.ase.uc.edu/~pnagy/ClassNotes/AEEM7028 Ultrasonic NDE/.
Permanent Citation