Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor with Activated Sludge Recycle

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
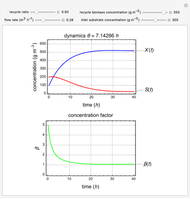
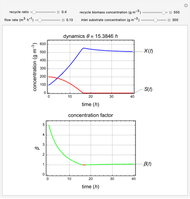
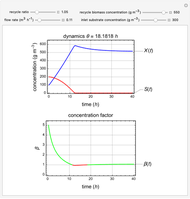
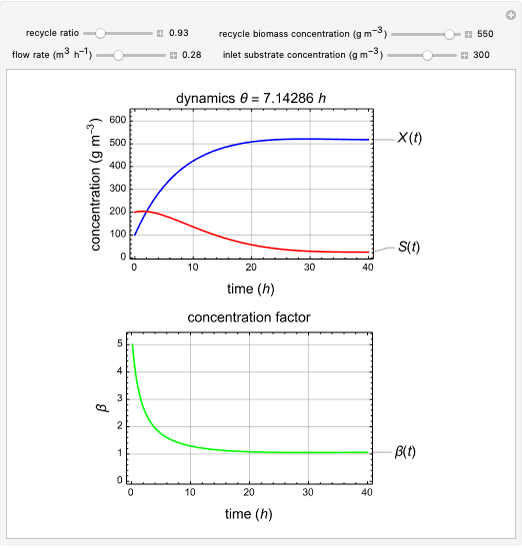
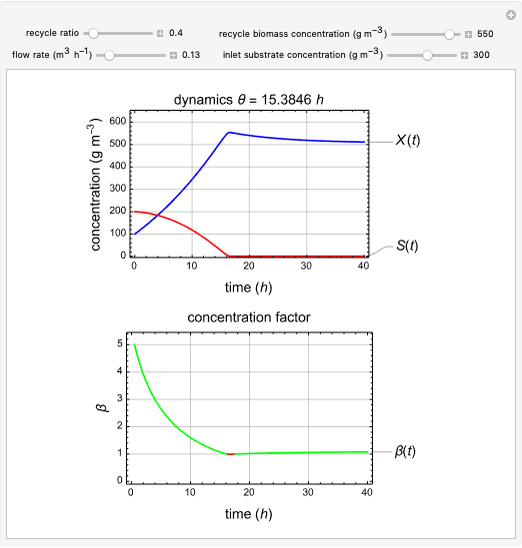
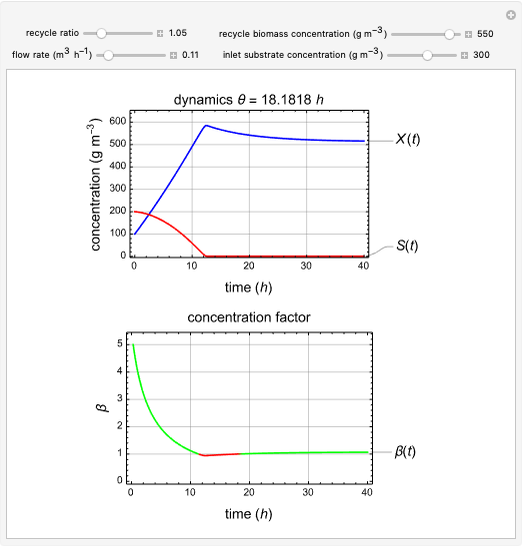
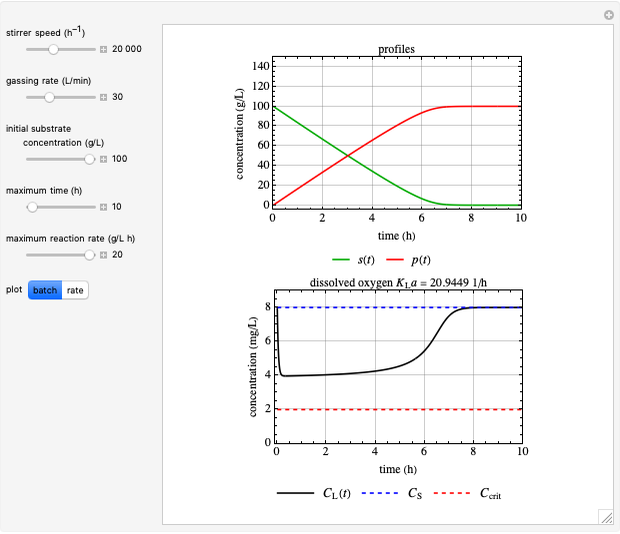
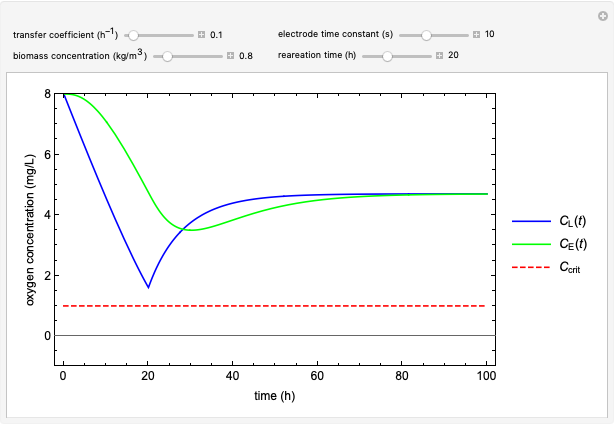
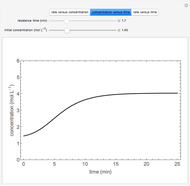
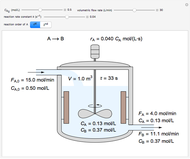
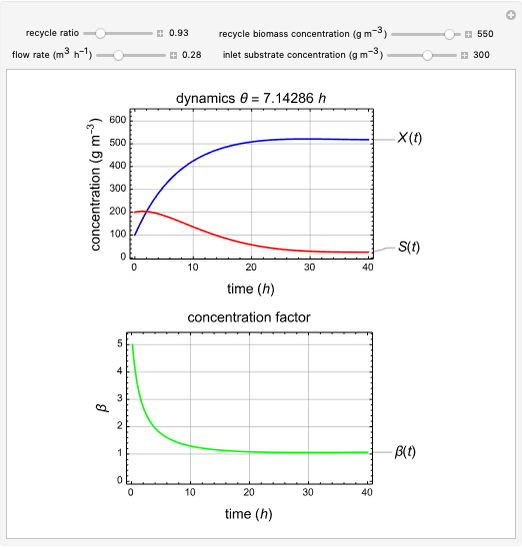
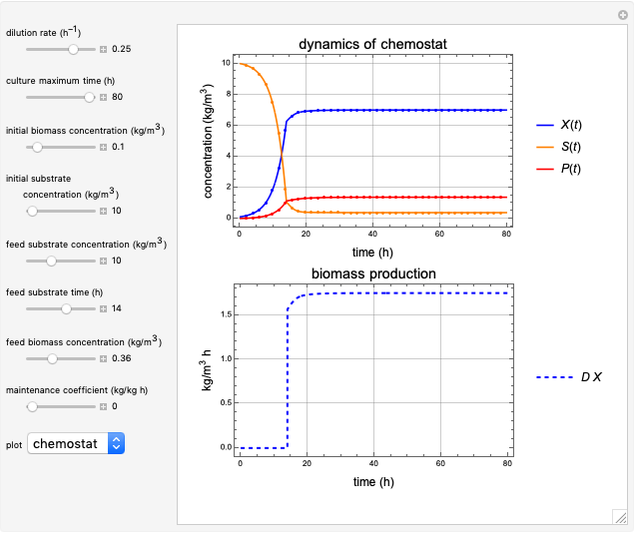
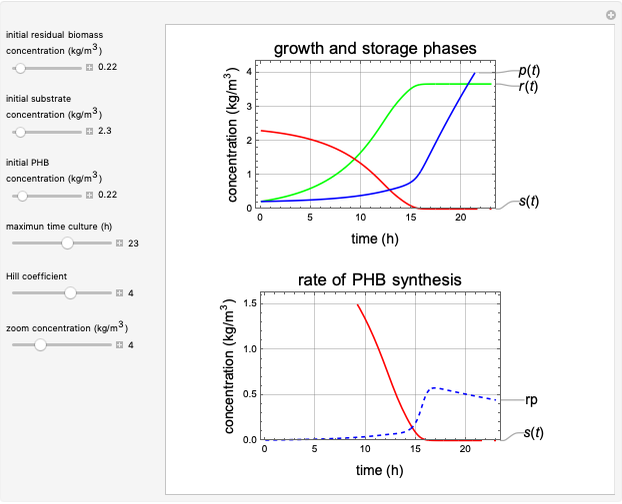
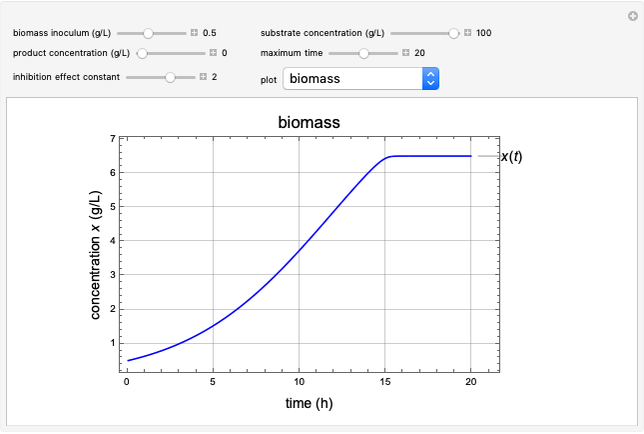
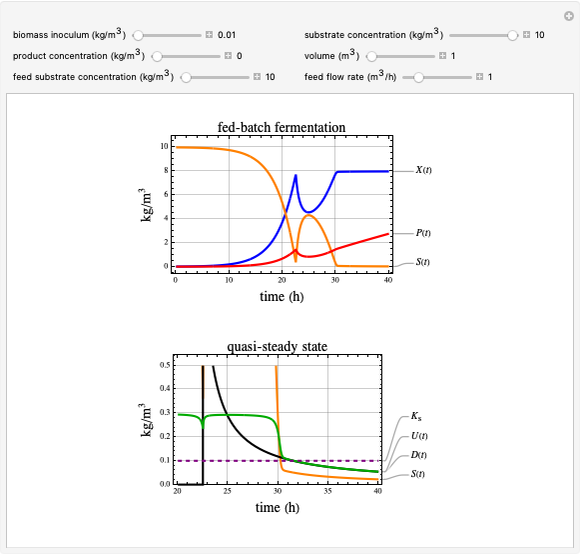
This Demonstration considers a model for the dynamics of a continuous stirred aeration tank processing activated sludge.
[more]
Contributed by: R. Ricardo Sánchez (August 2022)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The volumetric flow rate entering and leaving the reactor  is the sum of the influent
is the sum of the influent  and recycle flow
and recycle flow  rates:
rates:
 .
.
The recycle ratio is defined by:
 .
.
Then:
 .
.
The reactor residence time is defined as the volume of the reactor divided by the volumetric influent flow rate:
 .
.
The concentration factor  is defined as the ratio of the recycle biomass to effluent biomass concentrations:
is defined as the ratio of the recycle biomass to effluent biomass concentrations:
 .
.
Notation:
 : biomass concentration in reactor (
: biomass concentration in reactor ( ),
),
 : substrate concentration (
: substrate concentration ( ),
),
 : sludge concentration factor (dimensionless),
: sludge concentration factor (dimensionless),
 : recycle ratio (dimensionless).
: recycle ratio (dimensionless).
The model is described in detail in [1, Exercise 3.3.2].
Suggestions for further exploration:
1. Vary the recycle ratio to see how the performance of the process is influenced.
2. Vary the values of the flow rate to see how the process is influenced.
Reference
[1] J. B. Snape, I. J. Dunn, J. Ingham and J. E. Prenosil, Dynamics of Environmental Bioprocesses: Modelling and Simulation, New York: VCH, 1995.
Permanent Citation