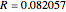Ideal Gas Law Solver

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
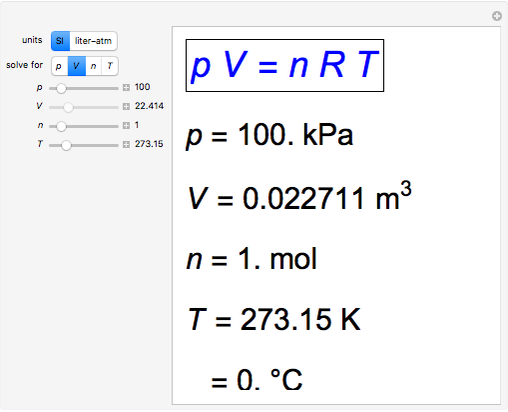
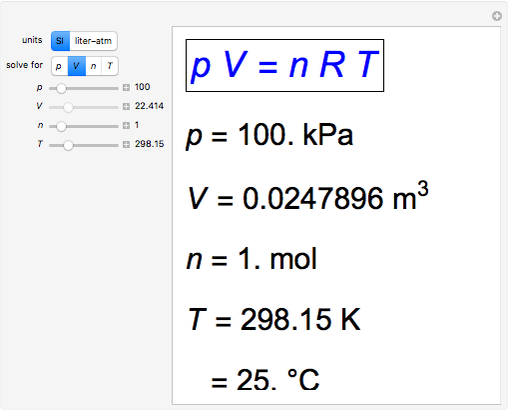
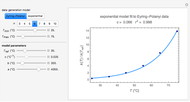
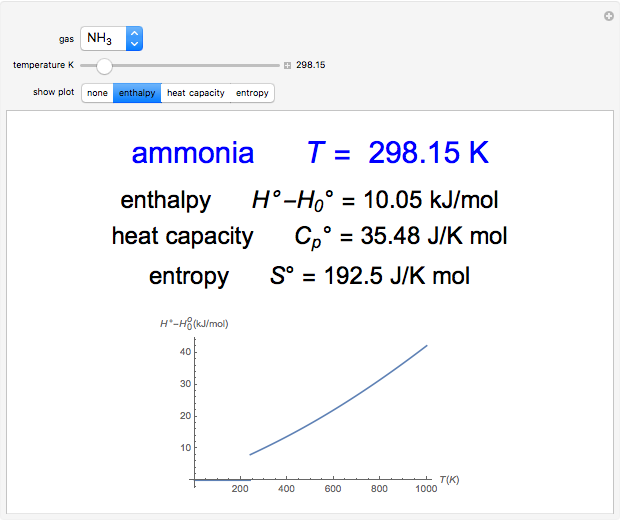
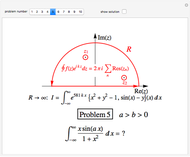
In this Demonstration, you can solve for any of the four variables in the ideal gas law, 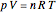 , given the other three. In SI units the pressure
, given the other three. In SI units the pressure 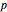 is expressed in pascals (Pa), equal to
is expressed in pascals (Pa), equal to 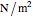 . Since one standard atmosphere equals 101.325 kPa, the SI pressure units are given in kPa. Volume
. Since one standard atmosphere equals 101.325 kPa, the SI pressure units are given in kPa. Volume 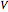 is in
is in 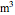 , temperature
, temperature 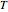 in K, and number of moles
in K, and number of moles  in mol. The universal gas constant
in mol. The universal gas constant 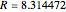 J/K mol (it is divided by 1000 so
J/K mol (it is divided by 1000 so 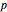 comes out in kPa).
comes out in kPa).
Contributed by: S. M. Blinder (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
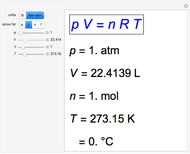
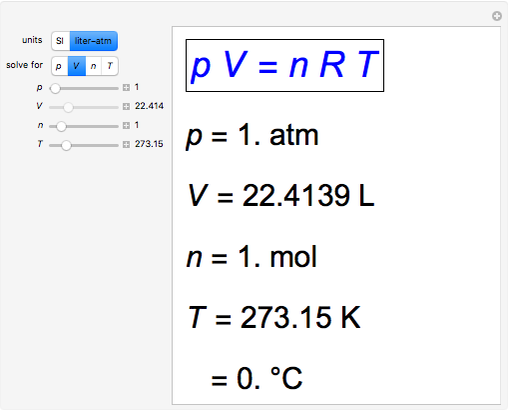
Snapshot 1: traditional definition of standard state: 1 atm, 0°C; gives well-known molar volume, 22.4 L
Snapshot 2: an alternative new definition, with 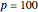 kPa = 1 bar
kPa = 1 bar
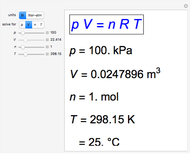
Snapshot 3: closer to room temperature, 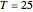 °C
°C
Permanent Citation