Dynamics of Seasonal Epidemics

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
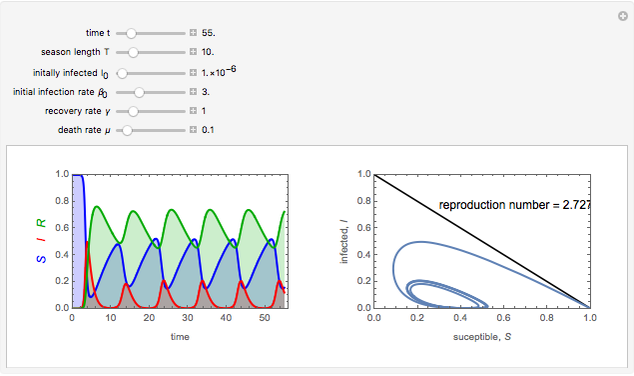
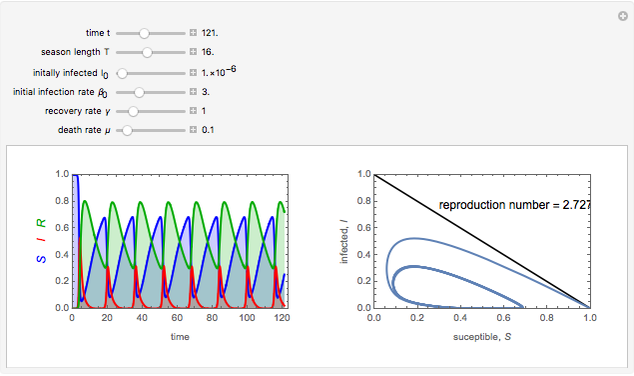
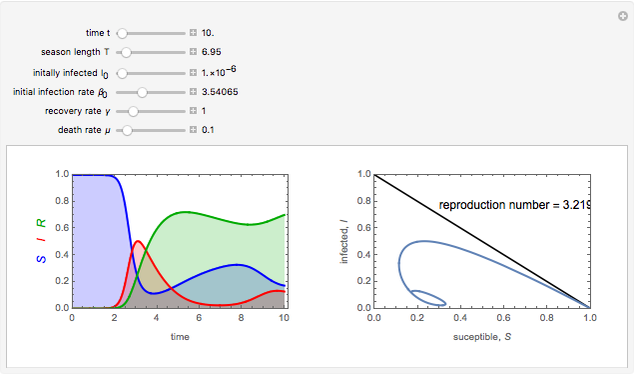
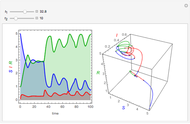
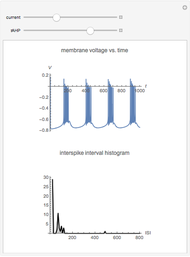
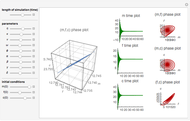
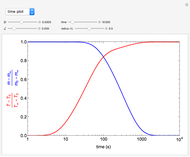
To study how the probability of getting a disease varies with the seasons of the year, this Demonstration analyzes a susceptibility-infection-recovery (SIR) model with a periodically varying infection rate. The model is a set of nonlinear differential equations with periodically varying parameters.
Contributed by: Clay Gruesbeck (November 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The periodically forced SIR model is:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
Here  ,
,  , and
, and  are the fractions of susceptible, infective, and recovered individuals in the population;
are the fractions of susceptible, infective, and recovered individuals in the population;  is the birth and death rate;
is the birth and death rate;  is the seasonally dependent infection rate; and
is the seasonally dependent infection rate; and  is the recovery rate. We take
is the recovery rate. We take  to be periodic;
to be periodic;  , where
, where  is the length of the infection season and
is the length of the infection season and  is a constant.
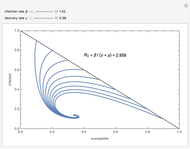
The reproduction number for this system is
is a constant.
The reproduction number for this system is  ; if the integral is greater than one, the disease will not disappear and may undergo interesting and complex phenomena of nonlinear parametric resonance [1].
; if the integral is greater than one, the disease will not disappear and may undergo interesting and complex phenomena of nonlinear parametric resonance [1].
You can vary the time window of observation, the length of the infection season, the fraction initially infected, and the rates of initial infection, recovery, and death to follow the trajectory of the SIR system.
Reference
[1] Wikipedia. "Compartmental Models in Epidemiology." (Jul 2, 2012) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compartmental_models_in _epidemiology.
Permanent Citation