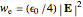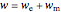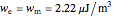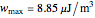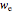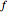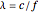Electromagnetic Wave Scattering by Conducting Sphere

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
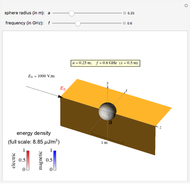
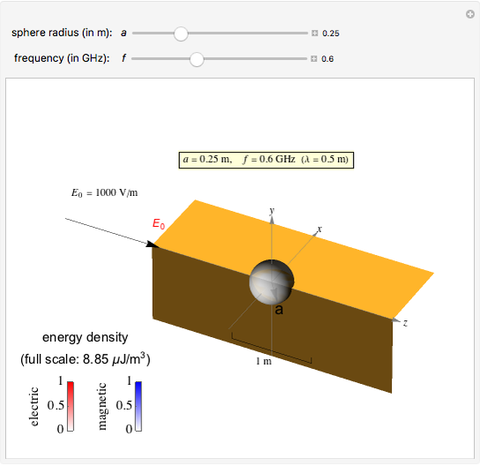
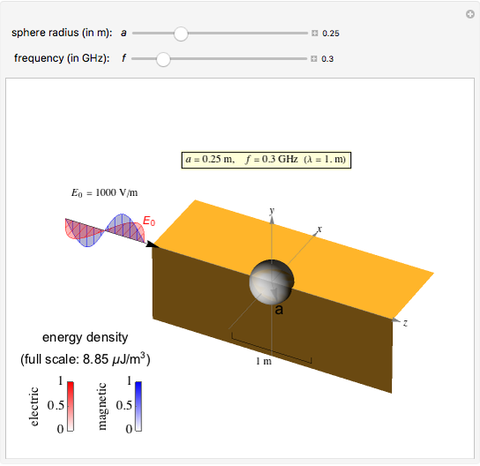
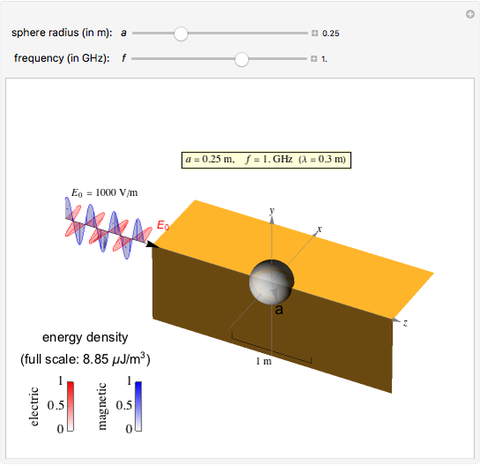
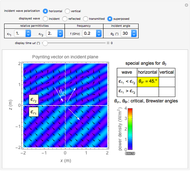
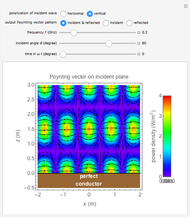
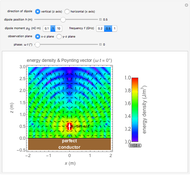
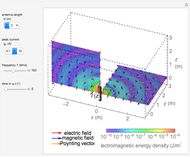
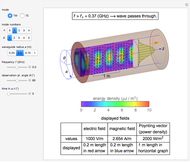
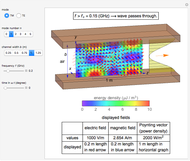
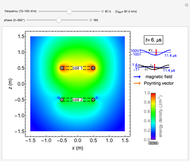
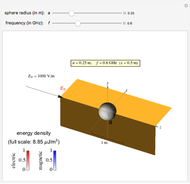
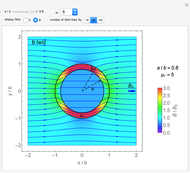
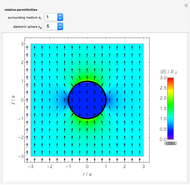
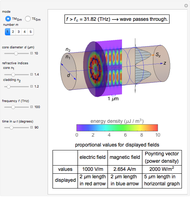
Electromagnetic waves can be scattered by electrical conductors. Consider a linearly polarized plane wave, with electric field in the  direction and incident in the
direction and incident in the  direction on a perfectly conducting sphere of radius
direction on a perfectly conducting sphere of radius  . The electric and magnetic fields of the incoming wave, expressed in Cartesian coordinates, are
. The electric and magnetic fields of the incoming wave, expressed in Cartesian coordinates, are 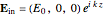 and
and 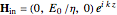 , where
, where  (
( and
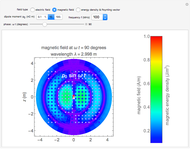
and  are the light velocity and impedance, respectively). The scattered fields
are the light velocity and impedance, respectively). The scattered fields  and
and 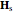 are best expressed in spherical coordinates
are best expressed in spherical coordinates  , using Legendre functions
, using Legendre functions 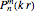 and spherical Hankel functions
and spherical Hankel functions  and taking account of the boundary conditions. The total fields are given by
and taking account of the boundary conditions. The total fields are given by 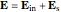 and
and 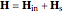 .
.
Contributed by: Y. Shibuya (September 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
References
[1] J. A. Stratton, Electromagnetic Theory, Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2007.
[2] W. K. H. Panofsky and M. Phillips, Classical Electricity and Magnetism, 2nd ed., Mineola, NY: Dover Publications, 2005.
Permanent Citation