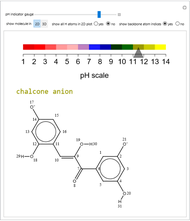
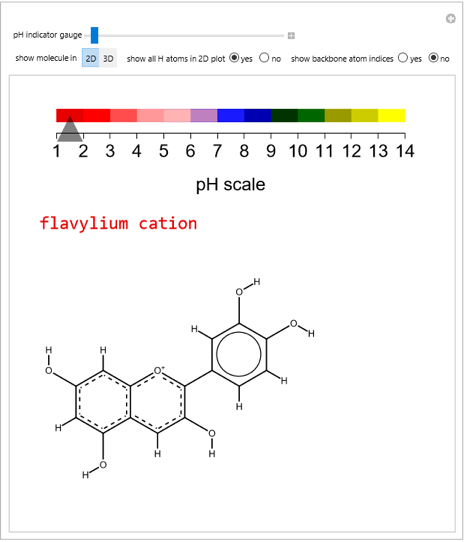
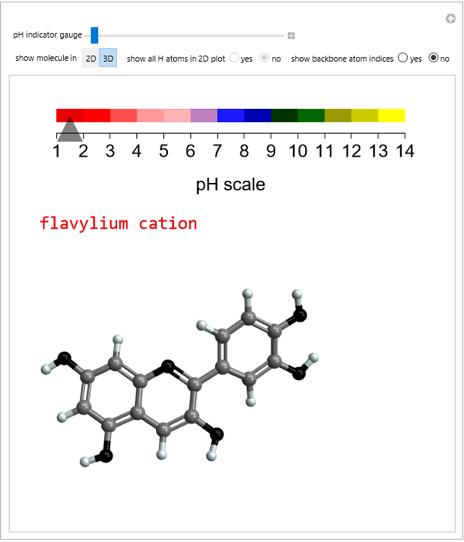
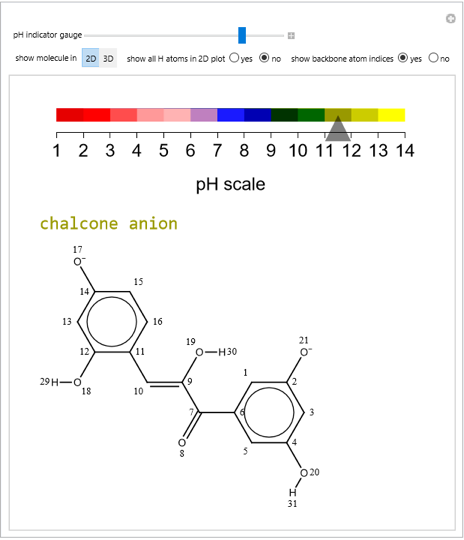
pH-Induced Changes in the Molecular Structure and Color of Anthocyanin Dyes

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
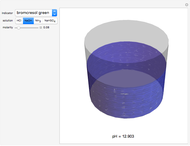
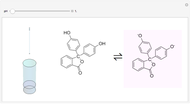
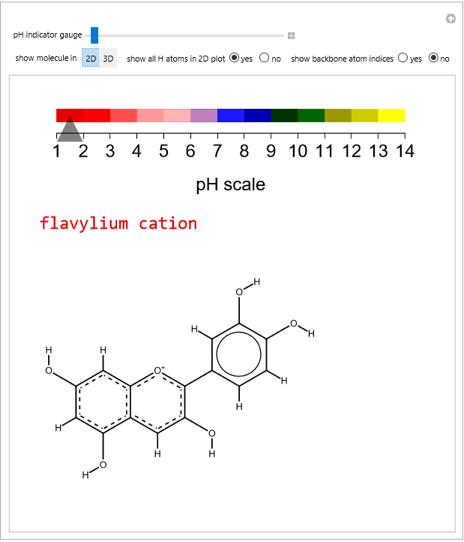
Cyanidin is a typical anthocyanin molecule found in red cabbage juice, fruits and flowers. This Demonstration shows how its molecular structure changes according to the pH of the surrounding chemical environment. As a response to this microscopic change, the color of the anthocyanin solution is also affected [1, 2]. This pH-responsive phenomenon, called halochromism, is why these compounds are used as natural pH indicators. Their color range can span from red (i.e. acid solutions with pH ⪡ 4) to yellow (extremely basic environments with pH ⪢ 7). As a further application, this property can be used to monitor the quality and safety of packaged food [3, 4] by using anthocyanins as dyes. Natural pH indicators such as litmus paper can exhibit different color scales depending on pH.
[more]
Contributed by: Jessica Alfonsi (August 27)
(Padova, Italy)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Details
[1] Wikipedia. "Anthocyanin." (Aug 11, 2023) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anthocyanin.
[2] German Wikipedia. "Cyanidin." (Aug 11, 2023) de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanidin.
[3] R. Priyadarshi, P. Ezati and J.-W. Rhim, "Recent Advances in Intelligent Food Packaging Applications Using Natural Food Colorants," ACS Food Science & Technology, 1(2), 2021 pp. 124–138. doi:10.1021/acsfoodscitech.0c00039.
[4] R. Abedi-Firoozjah, S. Yousefi, M. Heydari, F. Seyedfatehi, S. Jafarzadeh, R. Mohammadi, M. Rouhi and F. Garavand, "Application of Red Cabbage Anthocyanins as pH-Sensitive Pigments in Smart Food Packaging and Sensors," Polymers, 14(8), 2022 pp. 1629–1649. doi:10.3390/polym14081629.
[5] "Decimer." (Aug 11, 2023) decimer.ai.
Snapshots
Permanent Citation