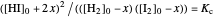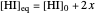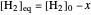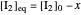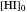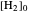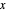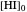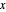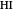Law of Mass Action and Chemical Equilibrium

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
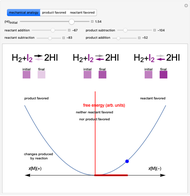
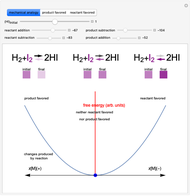
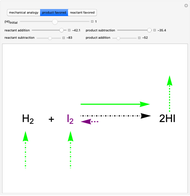
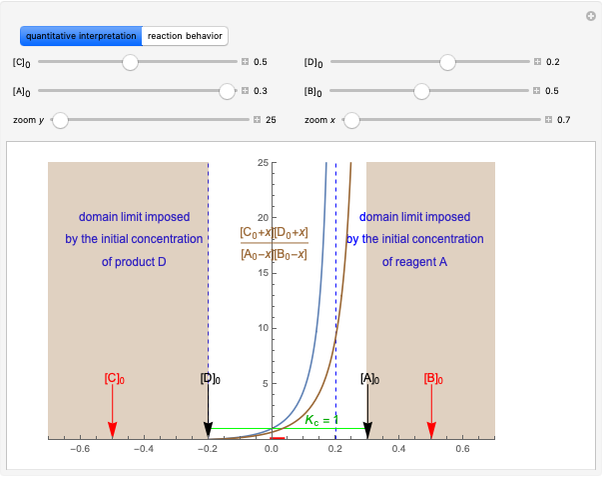
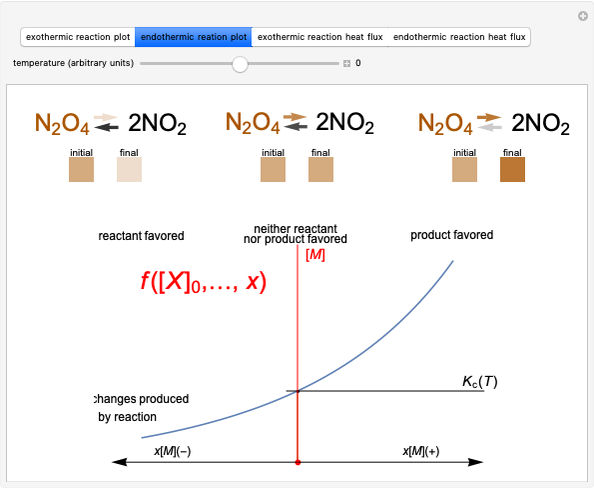
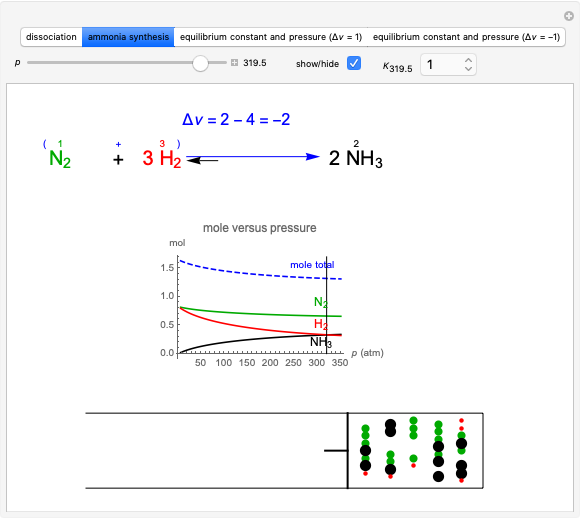
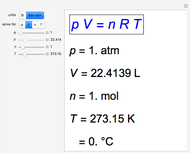
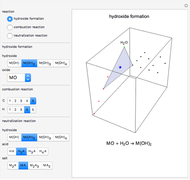
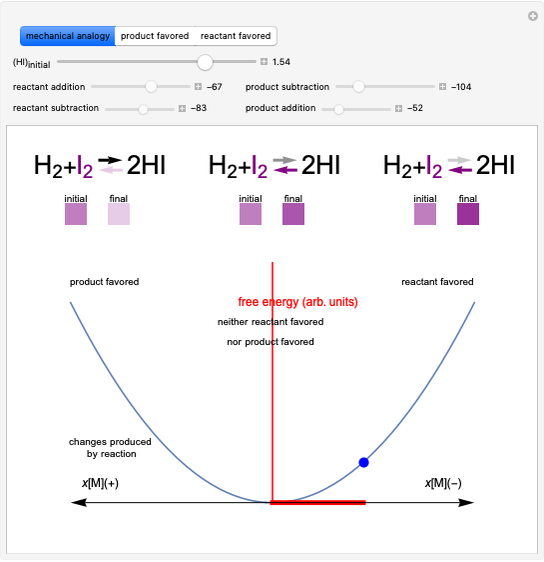
This Demonstration illustrates the law of mass action, which is an example of Le Chatelier's principle, that if a system in chemical equilibrium is disturbed it tends to change in such a way as to counteract the disturbance.
[more]
Contributed by: D. Meliga, L. Lavagnino and S. Z. Lavagnino (July 2020)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
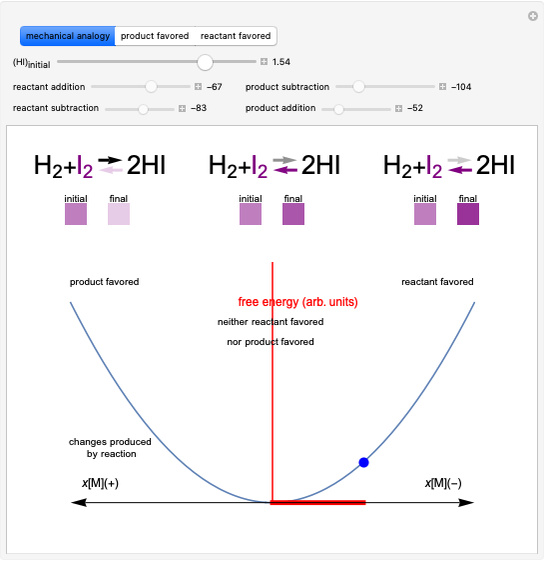
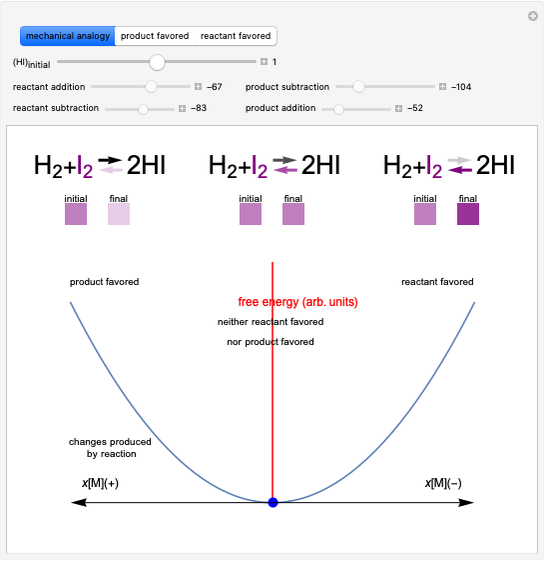
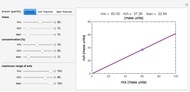
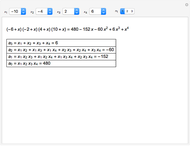
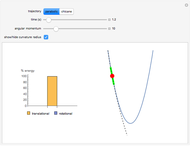
Snapshot 1: mechanical analogy for the chemical equilibrium; the initial concentration fulfills the equilibrium constant equation, so there is no variation
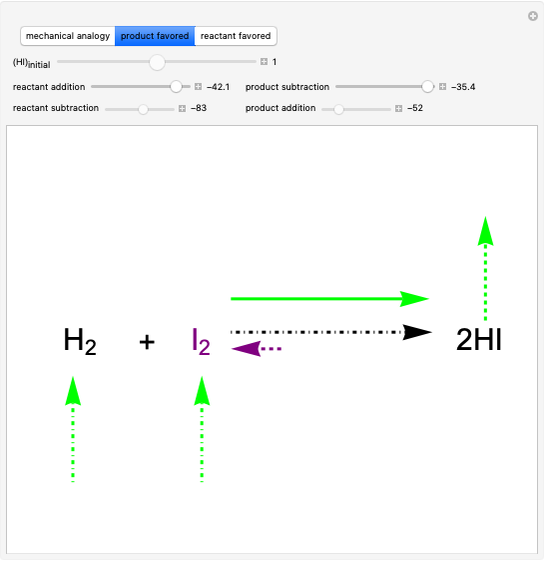
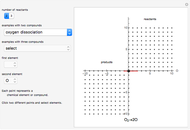
Snapshot 2: law of mass action: adding reactants or subtracting products in the equilibrium state causes a shift of the equilibrium toward the side of products
Snapshot 3: adding products or subtracting reactants in the equilibrium state causes a shift of the equilibrium toward the side of reactants
References
[1] C. H. P. Lupis, Chemical Thermodynamics of Materials, New York: North-Holland, 1983.
[2] S. V. Lavagnino. Chemical Equilibrium [Video]. (Jun 25, 2020) www.youtube.com/watch?v=TDBQOF7M-W8&list=PLswwssc6Q2yac7AM3x5UjmesLQaye-xMP&index=3.
Permanent Citation