Solvent Polarity in SN1 and SN2 Reactions

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
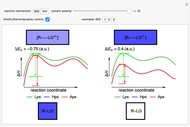
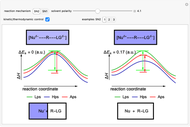
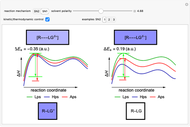
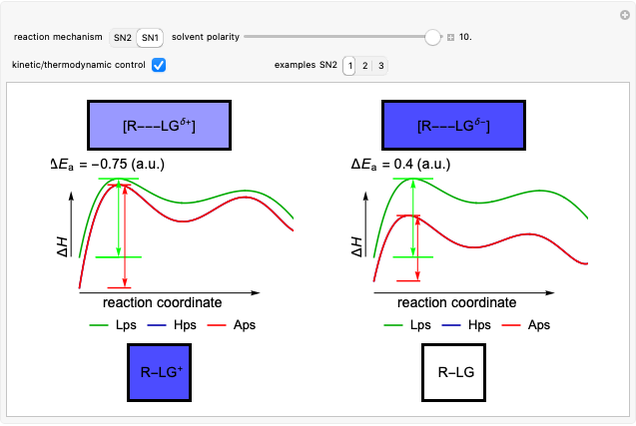
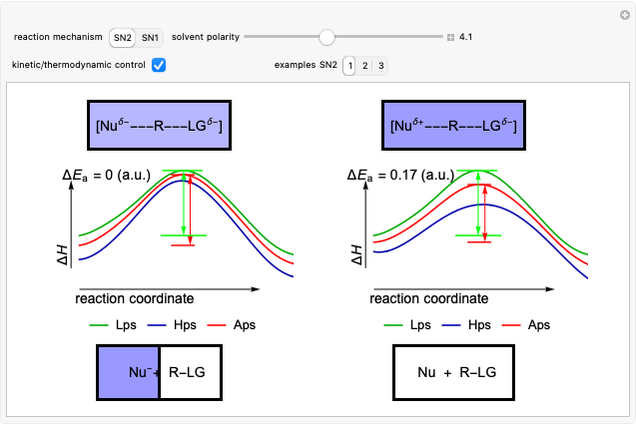
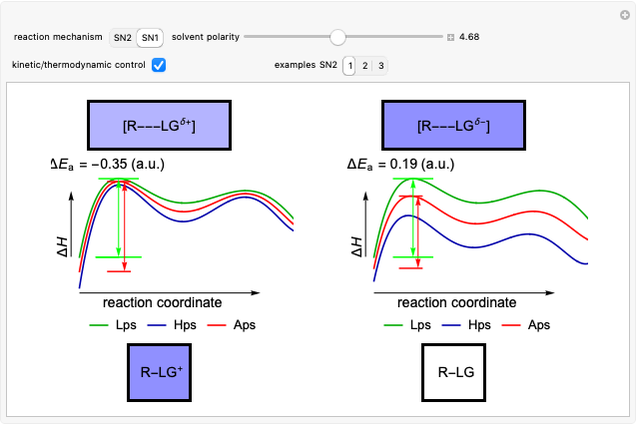
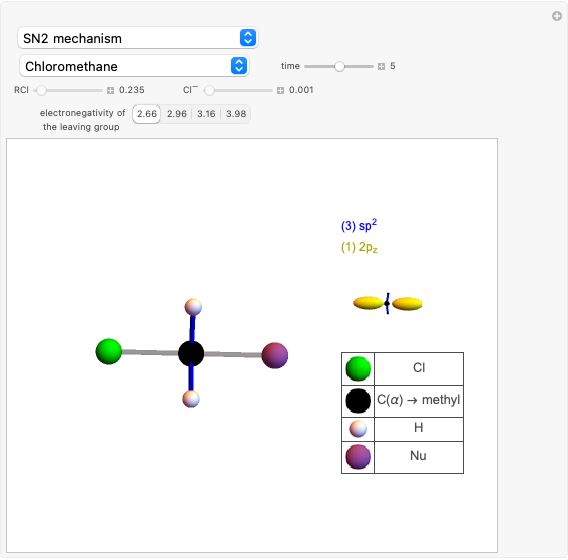
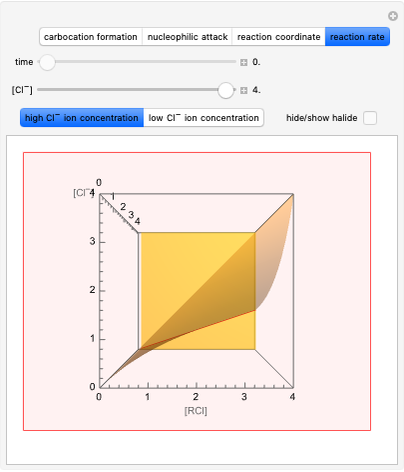
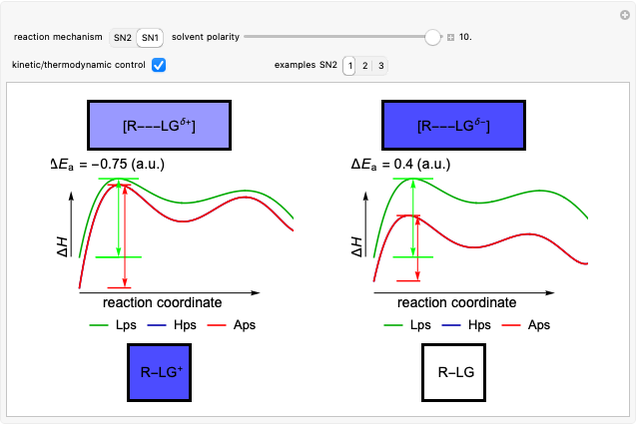
This Demonstration shows how the solvent polarity influences the nucleophilic substitution in both SN1 and SN2 reaction mechanisms [1].
[more]
Contributed by: D. Meliga, V. Giambrone, L. Lavagnino and S. Z. Lavagnino (October 12)
With additional contributions by: F. Calcagno
(ITIS A. Artom, Asti)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Details
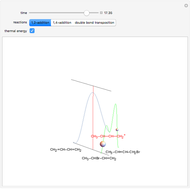
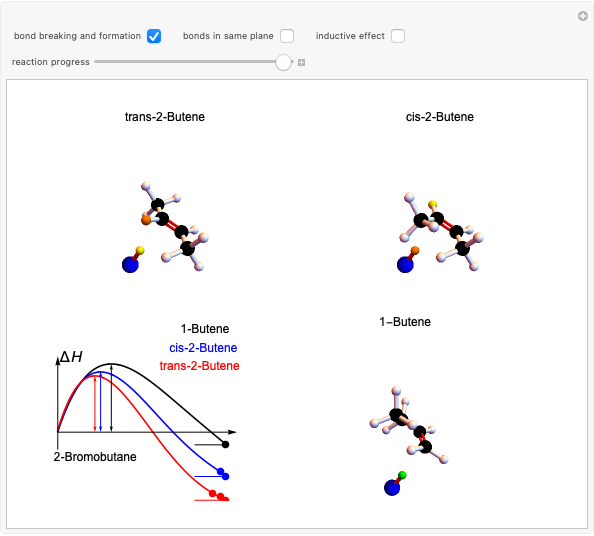
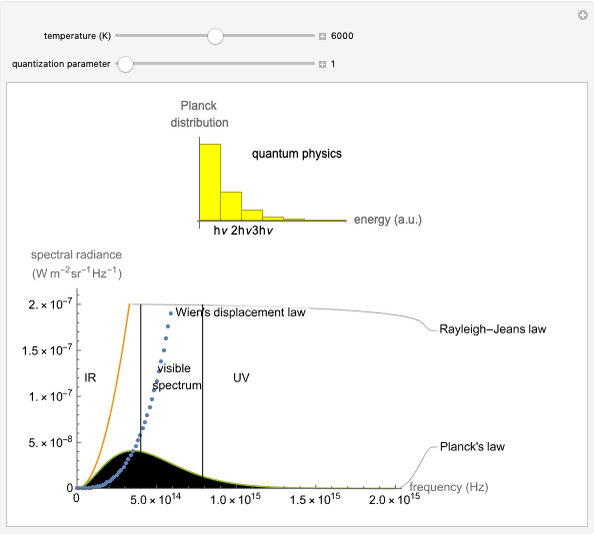
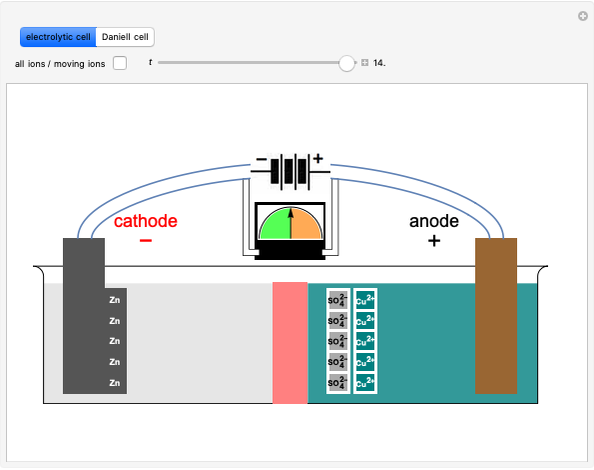
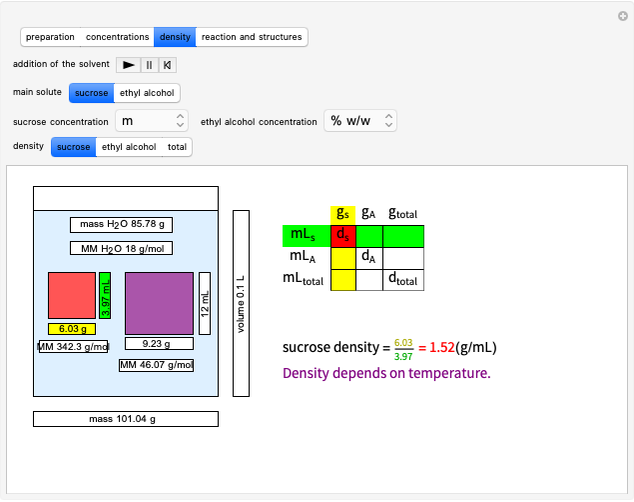
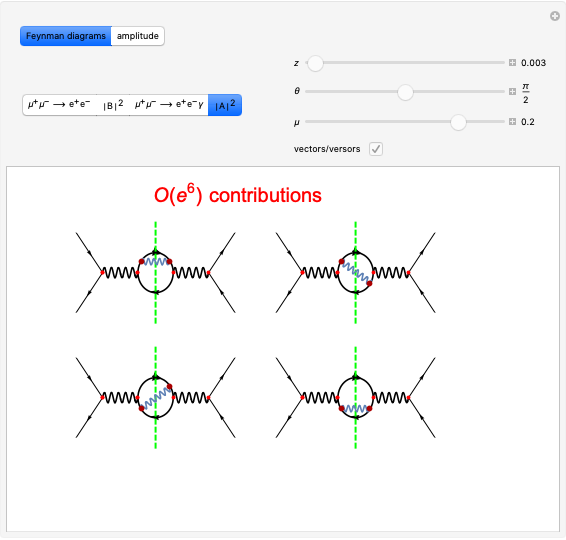
Snapshot 1: in an SN2 reaction, increasing solvent polarity changes the interactions between molecules of the reactants and the transition state; on the left an increase in the activation energies causes a decrease in the reaction rate; on the right, the opposite occurs
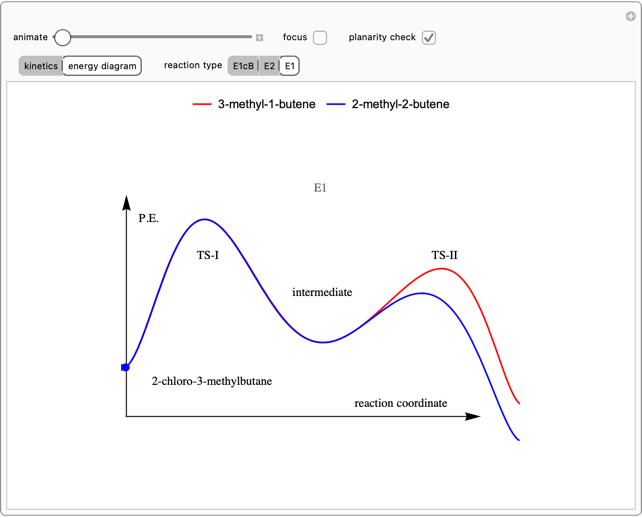
Snapshot 2: in an SN1 reaction, we can observe two maxima, showing the presence of two reaction pathways; only the first one is relevant to the reaction rate (bottleneck approximation) [1]
Snapshot 3: for the cases considered, the change in polarity does not appreciably affect the heat exchanged in the reactions
References
[1] S. Z. Lavagnino. Effetto solvente, nucleofilia reattività alogenuri alchilici [Video]. (Sep 14, 2023) www.youtube.com/watch?v=xK7BwLAbrIY&list=PLswwssc6Q2yYoP_INHmbmouyxW8oP _Gib&index=49.
[2] E. V. Anslyn and D. A. Dougherty, Modern Physical Organic Chemistry, Sausalito, CA: University Science, 2006.
Snapshots
Permanent Citation